![]()
In project management, effective resource management is crucial for success. Whether it’s human resources, materials, or equipment, the ability to allocate resources efficiently can make or break a project. Similar to the Work Breakdown Structure (WBS), the Resource Breakdown Structure (RBS) serves as a vital tool to organize project resources. It is an integral part of project planning, which involves considering factors like time, cost, and scope.
In this blog, we look at Resource Breakdown Structures, how to create them, their benefits, and practical tips for implementation.
Table of Contents
- What is a Resource Breakdown Structure (RBS)?
- A resource breakdown structure example
- Work Breakdown Structure (WBS) vs. Resource Breakdown Structure (RBS)
- What are the benefits of RBS in project management?
- Who typically creates an RBS?
- When should resource breakdown structures be created?
- How to make an RBS?
What is a Resource Breakdown Structure?
A Resource Breakdown Structure (RBS) is a hierarchical framework that systematically categorizes and organizes all essential project resources. It provides a detailed inventory of resources ranging from human capital and equipment to materials, facilities, and financial allocations.
Unlike a mere inventory, the RBS serves as a strategic guide for project managers, facilitating efficient resource organization and allocation throughout the project lifecycle.
Moreover, the RBS complements the Work Breakdown Structure (WBS) by detailing the resources needed for each component, such as tasks, deliverables, and milestones. This enhances project planning and execution, ensuring comprehensive resource management.
A Resource Breakdown Structure Example
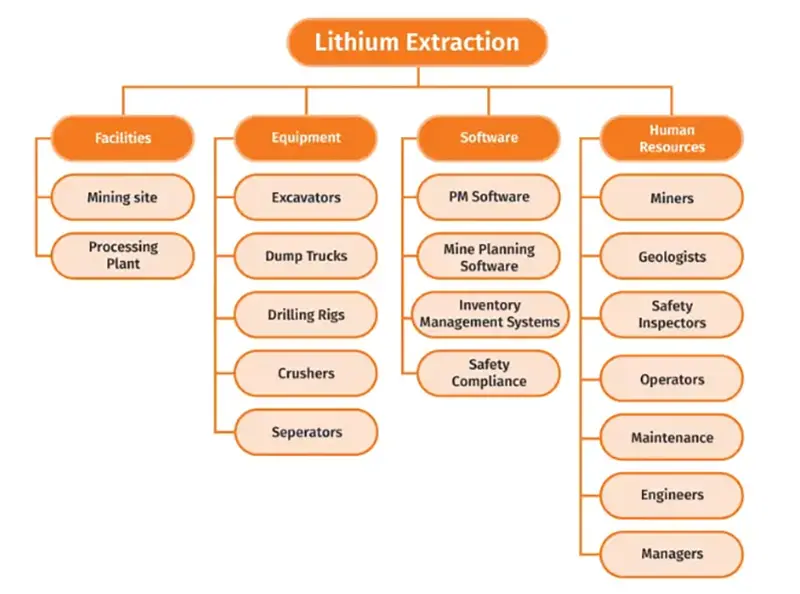
Figure 2. An RBS Example
As a Resource Breakdown Structure example, let’s look at a mining project that extracts lithium to see how resources are allocated and organized throughout the project.
At the core of the operation is the mining site itself, where excavation and extraction activities take place. Supporting this, there’s a processing plant to refine raw materials and prepare them for distribution.
Heavy equipment forms a significant part of the resources, including excavators, dump trucks, and drilling rigs. Additionally, there’s a need for specialized machinery like crushers and separators for ore processing.
Software tools like project management software are essential for monitoring operations and managing logistics. This includes mine planning software, inventory management systems, and safety compliance software.
Human resources are diverse and include miners, geologists, engineers, operators, maintenance personnel managers, and safety inspectors. Each plays a crucial role in ensuring smooth operations and adherence to safety standards.
Work Breakdown Structure (WBS) vs. Resource Breakdown Structure (RBS)
The WBS and RBS serve different roles in project management:
- Purpose: The WBS breaks down the project scope into tasks and deliverables, whereas the RBS organizes the resources required to complete those tasks.
- Focus: The WBS defines what needs to be done, while the RBS identifies how those tasks will be accomplished with the necessary resources.
- Order: Typically, the WBS is created first to outline the project scope, followed by the RBS to allocate the resources required for each task.
What are the Benefits of RBS in Project Management?
In the context of project management, RBS serves as a cornerstone for effective resource planning and execution. By breaking down resources into manageable categories and subcategories, RBS enables project managers to:
Plan Strategically
RBS empowers project managers to develop comprehensive project plans and schedules by offering a clear breakdown of the resources required for each task. Based on the upcoming projects, worker availability and experience, resources can be strategically assigned to jobs. This strategic approach not only ensures efficient resource deployment but also facilitates the alignment of project activities with timelines and milestones. By enabling a detailed assessment of resource requirements against project schedules, RBS optimizes scheduling accuracy and strategic decision-making for project success.
Optimize Resources and Decision-Making
RBS offers a strategic framework for identifying and assigning resources to project tasks, ensuring an informed resource allocation that aligns with project needs, priorities, and budget constraints. Additionally, this maximizes resource utilization while minimizing wastage, enhancing overall project efficiency. By accurately estimating the costs associated with project resources, RBS empowers project managers to make informed decisions, optimize budget allocation, and prevent cost overruns.
Collaborate and Communicate
RBS provides visibility into resource utilization and project progress, facilitating improved resource planning, allocation, and tracking. This is especially the case when combining the RBS with a WBS, to communicate who has to perform which part of the work. This transparency fosters effective communication and coordination among team members, which can result in enhanced project outcomes. With a well-defined RBS, project teams can develop a shared understanding of resource needs and availability, improving collaboration and operational effectiveness.
Proactively Mitigate Risks
Effective resource management is integral to mitigating risks in project management. By identifying resource dependencies and constraints, project managers can proactively plan for potential issues. They can develop contingency measures, monitor resource utilization, and integrate risk management practices effectively.
Monitor Resource Allocation
The RBS enables real-time monitoring of resources throughout the project lifecycle. This facilitates swift adjustments to resource deployment in response to changes in schedule or resource availability and ensures continuous project progression and leveled resources.
Resource breakdown structures are essential in project management, providing a structured framework for resource planning and allocation. By optimizing resource utilization and mitigating risks, RBS ensures project efficiency and success. As projects grow more complex, RBS remains a vital tool for achieving desired outcomes.
Now that we’ve explored the benefits of RBS, let’s dive into who is responsible for creating it and when it is typically developed.
Who Typically Creates an RBS?
Project managers and cost engineers typically craft resource breakdown structures but actively seek input from various team members. By pooling together insights and expertise, the team can break down the project into tasks and determine the resources needed for each one. This collaborative effort ensures a clear understanding of the project scope and aids in effective resource planning when multiple contractors and vendors are involved.
When Should Resource Breakdown Structures Be Created?
Timing is crucial when it comes to creating a resource breakdown structure. Ideally, project managers should develop RBS during the early stages of project planning, alongside other foundational project management processes such as defining project scope and objectives. By establishing a RBS early on, project teams can lay a solid foundation for resource planning, allocation, and management throughout the project lifecycle.
This typically occurs after creating the Work Breakdown Structure (WBS), which serves as a framework for identifying project tasks and deliverables. The team then uses the latter to determine the resources needed for each task within the RBS. Therefore, creating the RBS shortly after developing the WBS ensures alignment between project tasks and the resources required to execute them effectively.
How To Make an RBS?
To begin creating the Resource Breakdown Structure, it’s essential to understand its format and purpose. Much like the Work Breakdown Structure, the RBS requires an estimation of resources needed for each task in the project. Thus, having a comprehensive task list is crucial for collecting the necessary resources.
The Resource Breakdown Structure typically takes the form of a tree diagram, resembling the structure of the WBS. At the top of the diagram lies the project’s final deliverable, representing the overarching goal. Below this main deliverable, the RBS branches out into individual categories of resources. These branches represent resource types essential for project execution, such as the project site, equipment required, and the team responsible for project implementation.
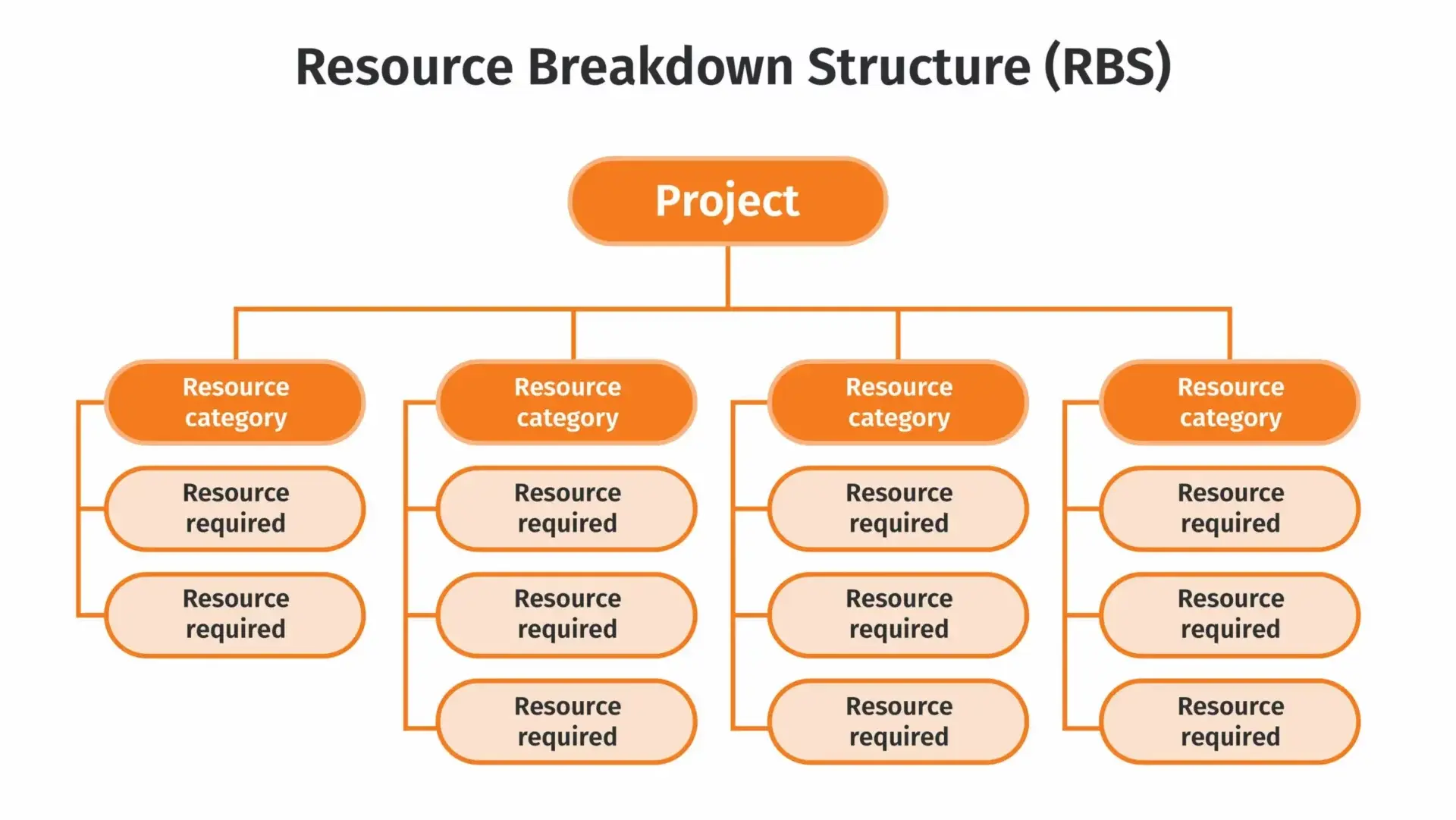
Figure 1. A simplified RBS
With this understanding of the RBS format and purpose, let’s delve into the steps for creating one effectively.
1. Identify Resource Categories
Begin by identifying the primary categories of resources required for the project. Common resource categories include human resources (personnel), materials, equipment, facilities, and any other assets necessary for project execution.
2. Break Down Resources
Once you have identified the resource categories, break down each category into more granular subcategories or resource types. For example, under the “human resources” category, you may have subcategories such as project managers, engineers, technicians, etc. Similarly, under the “materials” category, you may have subcategories like raw materials, supplies, etc.
3. Organize Resources Hierarchically
Organize the resources hierarchically, starting with broader categories at the top level and progressively breaking them down into more detailed subcategories as you move down the hierarchy. This hierarchical structure provides a clear and systematic overview of all resources involved in the project.
4. Map Resources to Project Tasks
Align the resources with the tasks identified in the WBS. Determine the resources needed for each task and ensure their appropriate allocation. This step helps in establishing a direct link between project tasks and the resources required to accomplish them.
5. Review, Refine, and Address Resource Risks
Continuously review and refine the RBS to ensure it accurately reflects project requirements, resource dependencies, and potential risks. Collaborate with relevant stakeholders, including project team members and subject matter experts, to validate resource allocations and make any necessary adjustments.
Additionally, identify and address potential resource risks, such as scarcity, dependencies, or potential disruptions. Analyze the factors contributing to these risks and integrate risk action plans within the RBS to mitigate and manage them effectively. By incorporating risk management into the refinement process, project teams can enhance the robustness of the RBS and improve resource allocation strategies, ultimately contributing to project success.
Streamline Resource Management with Cleopatra Enterprise
Cleopatra Enterprise’s work pack management software centralizes all your project planning into one streamlined platform. With real-time dashboards and updates, plus enhanced transparency, your team can easily track activities, collaborate effectively, and stay aligned. Say goodbye to scattered spreadsheets and disorganized workflows, Cleopatra ensures your project data is organized and accessible, making planning and execution seamless and efficient.
Request a demo today to see how Cleopatra can optimize your project planning.
This guide will walk you through the critical aspects of cost estimation, including key principles, the importance of…
In project management, a Cost Breakdown Structure (CBS) is a vital view used to organize and track expenses…
Related resources

Work Breakdown Structures (WBS): the correct philosophy
Dig into the Work Breakdown Structures for assigning the work-packages / deliverables and apply the correct cost control philosophy.
Read blog article
Resource-Based vs Activity-Based Estimating Software
The pros and cons of Resource based estimating and activity based estimating.
Read blog article